Parotidectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove part or all of the parotid gland, which is located near the ear and plays a role in saliva production. This procedure is typically indicated for the treatment of tumors or other abnormalities within the parotid gland, which may be benign or malignant. During a parotidectomy, the surgeon makes an incision along the jawline, carefully dissecting the facial nerve that runs through the gland to avoid damage. Depending on the extent of the condition, a portion or the entire parotid gland may be excised. Following removal, the incision is closed with sutures, and drainage tubes may be inserted temporarily to prevent fluid buildup. Parotidectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at removing all or part of the parotid gland, which is the largest salivary gland located in the cheek area. It's typically performed to treat tumors or alleviate symptoms caused by conditions such as chronic infections or stones within the gland. The surgery is conducted under general anesthesia, and the extent of gland removal depends on the nature and location of the pathology. The procedure involves making an incision along the jawline, carefully dissecting the gland from surrounding structures, and ensuring preservation of important nerves such as the facial nerve to maintain facial function. Following the removal of the affected portion, the incision is closed with sutures, and a drain may be inserted to prevent fluid buildup. Recovery generally involves pain management, monitoring for complications such as facial weakness or infection, and gradual return to normal activities under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Physical therapy and facial exercises may also be recommended to aid in restoring facial muscle function postoperatively.
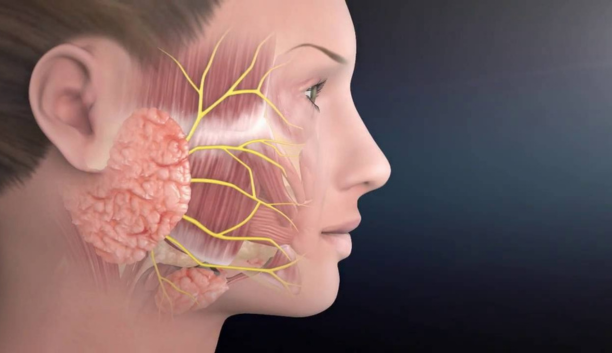
After surgery, patients may experience temporary facial weakness, numbness, or swelling, which typically resolve as the facial nerve and tissues heal. Complications such as infection, facial nerve damage, or salivary fistulas (abnormal connections between the mouth and skin) are possible but rare with careful surgical technique. Postoperative care involves pain management, wound care, and monitoring for signs of complications. Long-term follow-up is necessary to monitor for recurrence and ensure optimal healing and function of the facial nerve and surrounding structures.