Septoplasty is a surgical procedure used to correct a deviated nasal septum, which is the cartilage and bone that divides the nasal cavity into two nostrils. A deviated septum can cause nasal obstruction, difficulty breathing, recurrent sinus infections, and snoring. Septoplasty aims to straighten the septum, improve airflow, and alleviate associated symptoms. During septoplasty: Anesthesia: The patient is typically placed under general anesthesia, although local anesthesia with sedation may also be used in some cases. Incision: The surgeon makes an incision inside the nostrils to access the nasal septum, avoiding any external scars. Septum Adjustment: Using specialized instruments, the surgeon straightens the deviated portions of the septum by removing or reshaping the cartilage and bone. The goal is to create a more symmetrical nasal passage and improve airflow. Closure: Once the necessary adjustments are made, the incisions inside the nostrils are closed with dissolvable sutures, and nasal packing or splints may be placed temporarily to support the septum during healing. Septoplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at correcting a deviated septum, improving nasal airflow, and relieving symptoms such as nasal congestion and difficulty breathing.
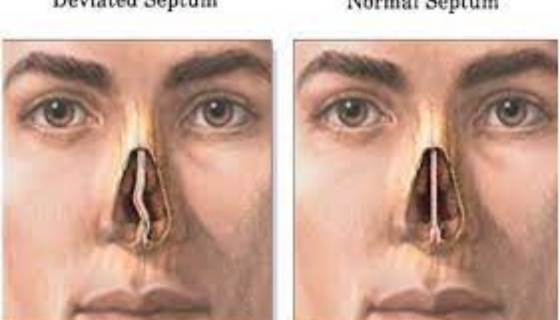
After septoplasty, patients may experience swelling, congestion, and mild discomfort, which can be managed with pain medications and nasal saline irrigations. It's essential to follow postoperative care instructions provided by the healthcare team, including avoiding strenuous activities and refraining from blowing the nose for a specified period. Septoplasty is generally considered safe and effective, with a high success rate in improving nasal airflow and alleviating symptoms associated with a deviated septum. However, as with any surgical procedure, risks such as bleeding, infection, nasal septal perforation, or changes in nasal shape or sensation may occur. It's crucial for patients to discuss the potential risks and benefits of septoplasty with their healthcare provider and to have realistic expectations for the outcomes. Regular follow-up appointments will ensure proper healing and monitor for any complications.